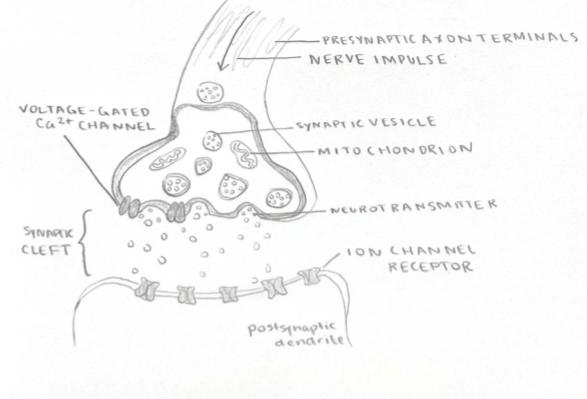
Function: The synapse is the site where neurons communicate with each other. It is the gap between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrite or soma of another. When an action potential reaches the synaptic terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, which diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
Structure: Synapses consist of the presynaptic terminal (which releases neurotransmitters), the synaptic cleft (the gap between cells), and the postsynaptic membrane (which receives the signal).
Other facts: Synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, is essential for learning and memory. Synapses can be excitatory or inhibitory, influencing whether the postsynaptic neuron will fire an action potential.
Back to Neuron